QR Codes: The Good, The Bad, and The Scammers

QR codes are becoming increasingly commonplace in Southeast Asia as a result of the ongoing influence of technology on the nature of monetary transactions. Quick Response (QR) codes are a particular kind of barcode that can be read by the camera on a smartphone to provide access to content or facilitate monetary transactions. In recent years, many shoppers and merchants have started to favour using these codes as a faster and more convenient payment option.
Southeast Asian financial institutions (FSIs) and banks have been early adopters of and beneficiaries of this nifty technology. QR codes allow FSIs to facilitate instantaneous transactions, enabling customers to use their smartphones to make purchases, send money to others, and have quick and easy access to their financial records by scanning these codes.
But there is always a cost to new technology, even when financial firms take extensive measures to assure their safety. For instance, one new form of fraud, called “QRishing,” has now emerged alongside the rise of QR-based payment systems.
QRishing – A Deceptive Game of Hide-and-Seek
There are many ways in which fraudsters can take advantage of QR codes to swindle their victims (who could be either individuals or businesses) and deception is the name of the game.
One of them, the proprietor of a pet shop in Malaysia known as Purrfect Pets, Faez, shared how he had to deal with a customer who attempted to swindle his business. The need for caution and vigilance in order to avoid falling for a QRishing scam is highlighted.
Faez advised business owners to stay vigilant and always double-check a QR transaction
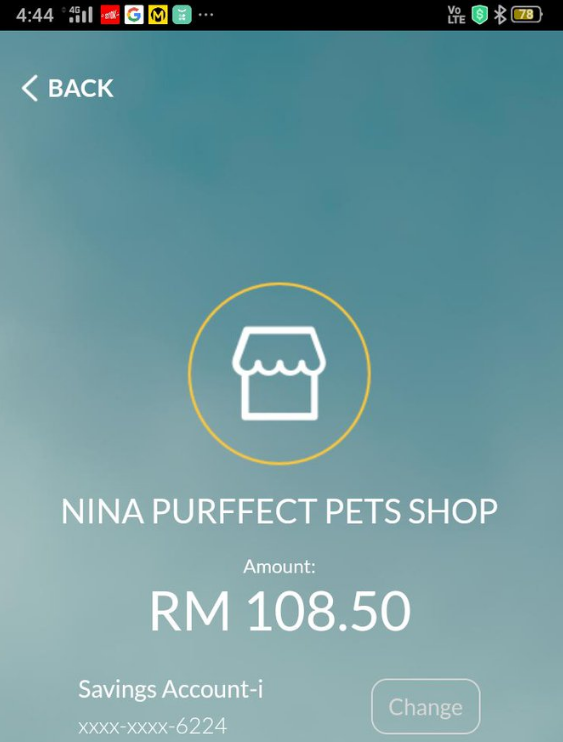
Faez mentioned the transaction proof looks suspicious as there are no signs of a successful transaction
QR code phishing occurs when a bad actor uses a QR code as a means to trick people into sharing personal or financial information. Phishers can use forged QR codes to impersonate legitimate businesses in an effort to get sensitive information. More worryingly, hackers might even replace genuine QR codes with fake ones to trick unsuspecting victims.

QR Codes are everywhere from a simple menu to a fully pledged marketplace
In the game of QR code phishing, scammers typically (or strategically) install fraudulent codes in locations where honest users would naturally go for authentic ones. For example, stickers with fake QR codes might be placed on parking meters, leading drivers to believe they can pay for parking at the meters via a bogus “Quick Pay Parking” website as part of a ploy to get them to provide their financial details. This was exactly what happened when illegally parked automobiles in China were tagged with false parking tickets that use QR codes to trick drivers into visiting a malicious website to pay their fees.

Digital QR codes are also a target of cybercriminals, as was witnessed in Germany when users of online banks were sent emails with malicious QR codes created to steal their banking credentials. Meanwhile, scammers in the Netherlands used QR codes to exploit a legitimate feature of ING Bank’s mobile banking application meant to enable a secondary mobile device to access their account. ING Bank ended up having to pay compensation to customers affected by the QR code fraud.
These are just a few separate examples of the possible schemes that could be carried out by fraudsters by manipulating the simple vulnerabilities inherent in QR code usage.
Ultimately, the purpose of each QR code phishing scam is the same: To trick people into disclosing sensitive information or giving up their hard-earned money.
There are ways in which people and organisations can protect themselves from falling prey to such frauds? To find out, we reached out to cybersecurity experts to get their views on the matter.
QR-ality Check: Protecting Yourself From QR Code Scammers
It’s important to always be wary while scanning QR codes and look for signs of manipulation to prevent falling for these tricks. When making a purchase, it’s always a good idea to verify the store’s name and URL. Take caution while entering personal information after scanning a QR code. Anti-virus and anti-malware software should be installed on mobile devices, and apps should only be downloaded from trusted sources.
To avoid falling prey to a QRishing scam, industry experts recommend the following precautions:

Yeo Siang Tiong, Kaspersky’s General Manager for Southeast Asia, has spoken out about the growing problem of QRishing, saying that the industry has been actively implementing measures like education, authentication, reporting, and multi-factor authentication to better protect consumers and businesses from falling victim to this type of fraud.
Yeo suggests verifying the URL thoroughly for the presence of the secure protocol (https://) and utilising a robust QR scanning programme (like Kaspersky QR Scanner) to avoid falling prey to a QRishing scam.
“It’s vital to keep in mind that QR codes are a double-edged sword: Although they can make payments and transactions easier, they can also be used by cybercriminals to steal personal data and financial resources. Therefore, it is essential to be alert to the potential dangers and to take all appropriate measures to safeguard oneself,” Yeo said.

Beng Hai Sim, ESET’s Head of Technical Sales in the Asia Pacific region, notes that the necessity for contactless, digital touchpoints in the wake of the pandemic has contributed to the rise in the use of QR codes in recent years.
A reliable mobile security app with anti-phishing capabilities is recommended by Sim as an effective means of combating QRishing.
Since the danger landscape is ever-changing, Sim anticipates companies producing technological solutions will make aggressive attempts to remain ahead of hackers. Enhancing security features at different tiers, such as DNS filtering, for more thorough threat prevention is one way to do this.

According to Endava’s Delivery Partner, Adrian Bugaian, customers are the weakest link in the payment chain as banks and payment service providers continue to promote new payment options. Organisations should immediately implement mechanisms for customers to report suspected instances of fraud, and they should also bring on the proper technology partner to deliver agile solutions that better enable them to manage, automate, and optimise their data.
The foundation for efficient real-time company operation and innovation rests on the quality of the data used to provide insights. In the long run, organisations need to embrace a digital acceleration strategy, or the ongoing development of their existing technology stack, to guarantee that they can respond to and address QRishing threats in real-time.

According to David Ng, Trend Micro’s Country Manager for Singapore, the technology exists now to verify QR codes but this is of little use if the public does not know how to use it. For instance, people’s approaches to cybersecurity vary depending on the gadget they’re using. Anti-virus programmes, for instance, are more commonly installed on desktops and laptops than on mobile devices. If the same logic is used for QR code authenticators, then users and companies would be without crucial protections to keep their data and assets safe across all of their devices.
In addition, all sectors, since they are vulnerable to QRishing, need to encourage education and awareness together. In recent years, the proliferation of QR codes in the food and beverage business has put them in the crosshairs. Therefore, no one and no sector is safe from this type of deception.
Convenience or Conundrum
On the one hand, nobody can dispute the value of QR codes. They facilitate the quick processing of financial transactions, the transfer of funds, and the access to relevant financial data with ease. They also let businesses of any size accept digital payments, which is extremely useful for startups. Nonetheless, possible drawbacks should also be acknowledged, especially the heightened security risks or possibilities of fraud.
Despite the fact that QR codes provide numerous advantages due to their speed and ease, it is vital that you think about the risks involved. We mustn’t rush into universally adopting QR codes as a payment mechanism without first carefully considering the advantages and disadvantages. We must keep in mind that there is usually a cost associated with ease of use when using technology for our financial transactions.
The next time you scan a QR code, it’s worth thinking, are you actually being led to a legitimate page, or are you being scammed?




