Fake Human Verification Pages Deliver Lumma Stealer Malware, Warns CloudSEK

CloudSEK’s Threat Intelligence team has uncovered a new and advanced method of distributing the Lumma Stealer malware, which is targeting Windows users through fake human verification pages.
This technique, initially discovered by Unit42 at Palo Alto Networks, is currently being used to spread Lumma Stealer malware but could potentially be leveraged to deliver various types of malicious software.
How the Attack Works
Threat actors behind this campaign create phishing websites, often hosted on trusted platforms like Amazon S3 and CDN providers, to lure users into completing a fraudulent Google CAPTCHA verification. Upon clicking the “Verify” button, users are tricked into following these unusual instructions:
- Open the Run dialog (Win+R).
- Press Ctrl+V to paste the copied content.
- Press Enter. (For More Details. Read Full Report)
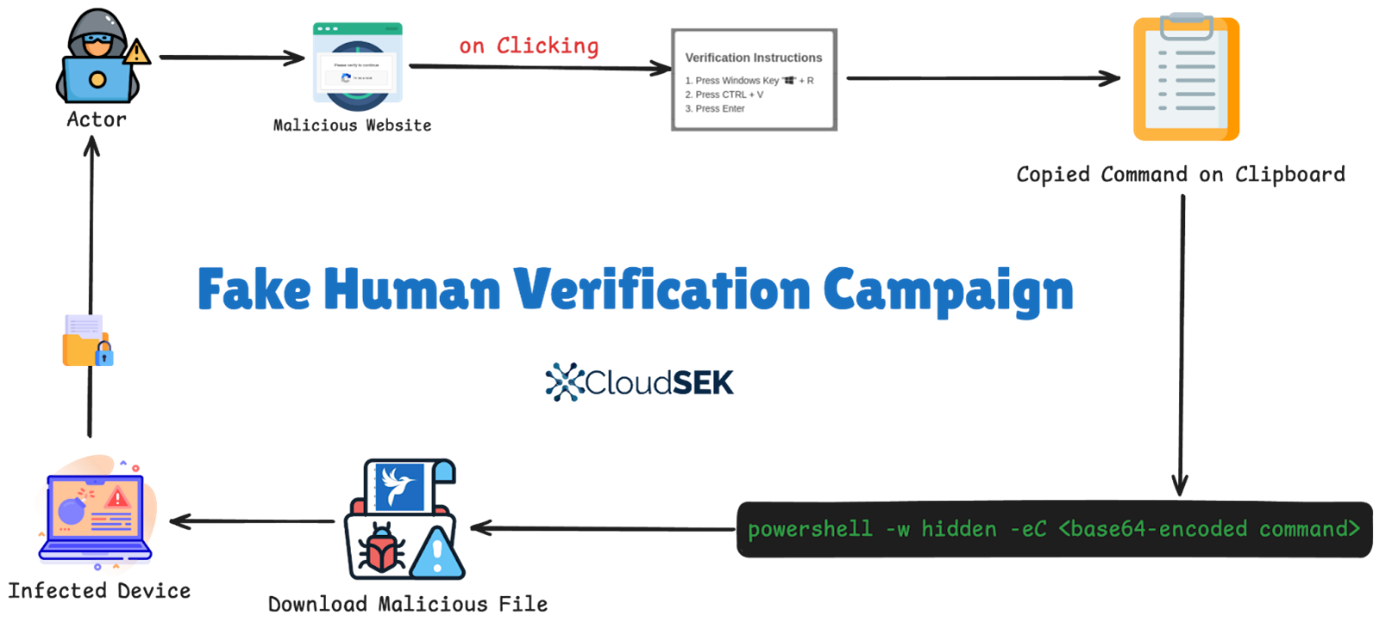
This action covertly executes a hidden JavaScript function, which copies a base64-encoded PowerShell command onto the user’s clipboard. When the user pastes and runs this command, the Lumma Stealer malware is silently downloaded from a remote server, compromising the victim’s system.
“This new tactic is particularly dangerous because it plays on users’ trust in widely recognised CAPTCHA verifications, which they encounter regularly online. By disguising malicious activity behind what seems like a routine security check, attackers can easily trick users into executing harmful commands on their systems. What’s more concerning is that this technique, currently distributing the Lumma Stealer, could be adapted to spread other types of malware, making it a highly versatile and evolving threat,” said Anshuman Das, Security Researcher at CloudSEK.
Technical Breakdown of the Lumma Stealer Malware
The infection chain typically follows this process:
- The user visits the fake verification page.
- A PowerShell script is copied to the clipboard through the deceptive CAPTCHA prompt.
- When the user executes the script, it runs PowerShell in a hidden window, downloading Lumma Stealer from a remote server.
The downloaded malware then establishes connections with attacker-controlled domains, posing a risk to users and their data. (For More Details, Read Full Report)
Key Observations
- Attackers use base64 encoding and clipboard manipulation to evade detection.
- Fake human verification pages have been hosted on well-known platforms like Amazon S3 and CDNs.
- The malware may download additional components, complicating detection and analysis.
- Although this campaign primarily targets distributing Lumma Stealer malware, it has the potential to deceive users into downloading various types of malicious files onto their Windows devices.
Recommendations for Users and Organisations
- Educate employees and users about this new social engineering tactic, particularly the danger of copying and pasting unknown commands.
- Deploy robust endpoint protection solutions capable of detecting and blocking PowerShell-based attacks.
- Monitor network traffic for suspicious connections to newly registered or uncommon domains.
- Regularly update and patch systems to reduce vulnerabilities exploited by Lumma Stealer.
CloudSEK’s investigation has uncovered several fake verification pages.
The full report includes a full list of malicious URLs and more detailed technical information.