The Cryptocurrency Drainer Hiding on Google Play

by Alexander Chailytko, Cyber Security, Research & Innovation Manager at Check Point Software Technologies

As digital assets become increasingly popular, so do the risks that come along with it. Despite improvements in cryptocurrency wallet security and growing user awareness about the dangers, cybercriminals continue to find increasingly sophisticated ways to deceive users and bypass security measures. Crypto drainers, which are malware designed to steal crypto assets, have become a popular method for attackers. Using phishing websites and apps that mimic legitimate cryptocurrency platforms, attackers fool users into authorising an illegitimate transaction, which allows the drainer to execute the transfer of digital assets to the perpetrators.
For the first time reported, these malicious tactics have also extended to mobile devices. Check Point Research (CPR) identified an application called WalletConnect on Google Play that leveraged a crypto drainer to steal users’ assets. Mimicking the legitimate Web3 open-source protocol WalletConnect, the malicious app, using advanced social engineering techniques and technical manipulation, deceived users into believing it was a safe way to transfer cryptocurrency. First uploaded to Google Play in March 2024, the app went undetected for over five months using evasion techniques and was installed over 10,000 times, stealing over US$70,000 in cryptocurrency from unsuspecting victims.
In this article, we explain how social engineering was used to deceive victims into downloading the drainer, break down the crypto drainer, and highlight the increasing sophistication of attacks, especially in decentralised finances.
Social Engineering Tactic in Apps
WalletConnect is an open-source protocol that securely connects decentralised applications (dApps) and cryptocurrency wallets. It was created to improve user experience when connecting dApps with crypto wallets. However, connecting with WalletConnect is often difficult for several reasons. Not all wallets support WalletConnect, and users often don’t have the latest version. Cleverly, attackers exploited the complications of WalletConnect and tricked users into thinking that there was an easy solution—the falsified WalletConnect app on Google Play.
The Deceptive Application
Once users downloaded and launched the malicious WalletConnect app, they were prompted to connect their wallet, assuming it would act as a proxy for Web3 applications that support the WalletConnect protocol.
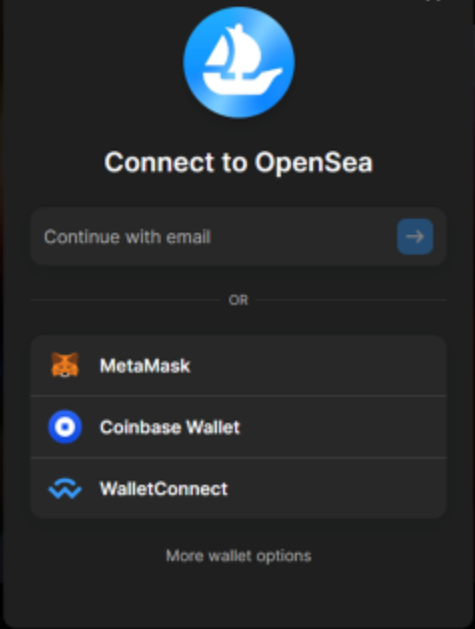
When the user selects the wallet button, the malicious app activates the chosen wallet and directs it to a malicious website. Users then must verify the selected wallet and are asked to authorise several transactions.
Each user action sends encrypted messages to the Command and Control (C&C) server and retrieves details about the user’s wallet, blockchain networks, and addresses. A sophisticated app, it withdrew the more expensive tokens before targeting less expensive ones performing the same process across all of the networks, to withdraw the victim’s more valuable assets first.
Unsuspecting Crypto Victims from Attacks
Check Point Research analysed the address from the WalletConnect app’s configuration from which the funds were stolen. Token transactions from over 150 addresses were identified, indicating at least 150 victims. There were very few outgoing transactions from the attackers’ wallets, with most of the stolen funds remaining in their addresses across various networks. According to blockchain explorer data, the total value of assets in the attackers’ wallets is estimated to exceed US$70,000.
Only twenty users whose money was stolen left negative reviews on Google Play, suggesting that there are still many victims who may still be unaware of what happened to their money. When the app received such negative reviews, the malware developers deviously flooded the page with fake positive reviews instead to mask the negative reviews, and make the app appear legitimate, to mislead other potential victims. Google Play has since removed the application.
Evading Detection
Attackers executed a sophisticated crypto-draining operation by combining social engineering and technical manipulation. They exploited the trusted name ‘WalletConnect’ and capitalised on users’ confusion surrounding connecting Web3 applications and crypto wallets, leading to significant cryptocurrency amassment without raising immediate suspicion.
This incident underscores the increasing sophistication of cybercriminal tactics, especially in decentralised finance, where users frequently depend on third-party tools and protocols to manage their digital assets. The malicious app’s effectiveness is further enhanced by its ability to avoid detection through redirects and user-agent checking techniques. Conventional tools like Google Search, Shodan, and automated checks often fail to identify such threats, as they depend on visible and accessible data that these apps intentionally obscure. This makes it nearly impossible for automated systems and manual searches to detect them.




