Reinforcing a Commitment: AWS Highlights Security as Top Priority, Promises Secure GenAI Innovation in APAC

Security is Amazon’s top priority.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) echoed this commitment to security in an exclusive virtual brief with media practitioners in Southeast Asia weeks after holding AWS re:Inforce 2024 in the US. The virtual brief, AWS re:Inforce 2024 ASEAN Security Briefing, outlined Amazon’s key announcements during the flagship conference and discussed in depth the company’s security initiatives to help customers in the region develop generative AI applications safely and securely.
Key Announcements from AWS re:Inforce 2024
Kimberly Dickson, Senior Worldwide GTM Security Lead for Detection and Response Services at AWS, facilitated the security briefing and started it off with a recap of these key announcements:
- Amazon GuardDuty Malware Protection for Amazon S3, now generally available, supports Amazon S3, enabling AWS customers to scan newly uploaded objects to Amazon S3 buckets to check for potential malware, viruses, and other suspicious uploads and then take corresponding action—isolating them before they can do any damage.
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) now provides easier, more secure sign-in access by supporting passkey as a second authentication factor. Passkeys use public key cryptography to enable strong, phishing-resistant authentication and are more secure than passwords. They are also based on FIDO standards. AWS IAM also supports built-in authenticators, like Touch ID on Apple MacBooks and Windows Hello facial recognition on PCs, for even more secure sign-ins. Passkey support aims to improve MFA usability and recoverability where clients use different IAM MFA methods to access their AWS accounts.
- AWS CloudTrail Lake now supports generative AI-powered natural language query generation that lets clients ask questions “as is.” This capability enables them to easily analyse their AWS activity events in CloudTrail Lake without having to write complex SQL queries. For instance, an AWS customer can ask, “How many errors were logged during the past week for each service, and what was the cause of each error?” to check for AWS API and user activity.
- AWS Audit Manager is a new version of AWS’ generative AI best practices framework that now provides visibility into customer’s generative AI usage on both Amazon SageMaker and Amazon Bedrock. This updated framework includes 110 controls across areas, like governance and data security, and also updates data source mappings and automated evidence collection for Amazon SageMaker.
“These announcements showcase the commitments AWS has made to ensure that customers are able to build generative AI and AI applications on top of AWS,” Dickson pointed out. “The addition of these features to our services leads us to these three key points: Firstly, AWS is the most secure cloud for generative AI. Secondly, customers are increasingly choosing AWS to build their generative AI applications because of our commitment to security. Lastly, customers are improving their security outcomes and building innovative generative AI applications on AWS.”
Security Is a Shared Responsibility—and AWS Is Taking Its Part Very Seriously
Despite AWS’ leading security capabilities, Dickson nonetheless emphasised the massive role of AWS customers in security where they must play a part, too, in securing their workloads—including those of the generative AI kind (see Figure 1).
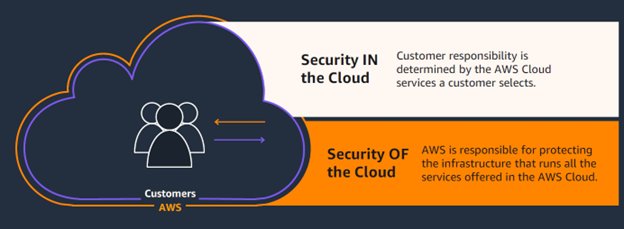
With this shared responsibility, clients are expected to be active participants in AWS’ defence-in-depth security strategy—one where multiple layers of protection are implemented to secure and safeguard a company’s most prized assets (which is usually data).
“When it comes to building these applications on AWS, we need to start with the basics, which is really thinking about applying a defence-in-depth strategy to generative AI workloads, starting with our shared responsibility model,” Dickson emphasised. “Customers need to understand the shared responsibility model between AWS and the workloads that they build on top of AWS.”
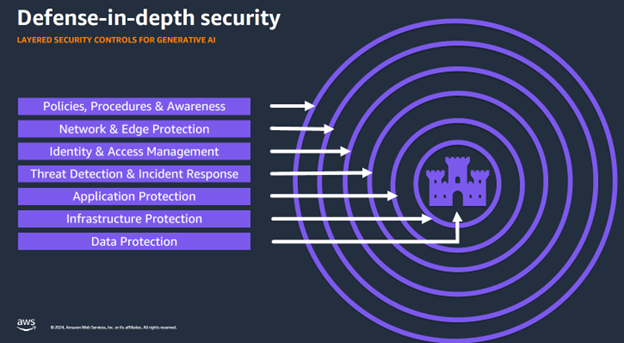
AWS’s defence-in-depth strategy is as multilayered as they come, starting with the outermost layer of security policies, procedures, and awareness. The Network and Edge Protection and Identity Access and Management layers follow, with four other layers—Thread Detection and Incident Response, Application Protection, Infrastructure, and Data Protection—fortifying this defence model (see Figure 2). With multiple layers, one breach won’t be the end of the world so to speak, as it will be contained by the other layers before it can do damage.
A Complete Platform for Generative AI Innovation
Aside from offering a secure platform, AWS also provides its customers with an entire, encompassing stack of generative AI tools, essentially giving them all they need to innovate and experiment with this game-changing innovation. Figure 3 outlines AWS’s generative AI stack.

Not for nothing then that many organisations, according to Dickson, are choosing AWS because “it provides a secure, private, and safe platform for them to run their AI workloads.” This is particularly true for companies in Southeast Asia, who are banking on the most secure cloud infrastructure globally to develop their innovative generative AI workloads. Three of them are Thailand’s Botnoi.ai, a generative AI text-to-speech voice and chatbot; Vietnam’s Arcanic.AI, an AI platform developer; and Singapore’s Temus, a digital transformation firm.
 |
 |
 |
|
Leverages AWS compute services to generate natural speech synthesis audios and text. |
Developing a culturally aware all-in-one AI platform for Vietnamese businesses by fine-tuning their LLM on Amazon Sagemaker.
|
Used Amazon Q Developer for its in-built privacy and security and built a Natural Capital Monetisation Platform that saw developer efficiency boosted by 35%, improving code quality, security scans, and maintainability. |
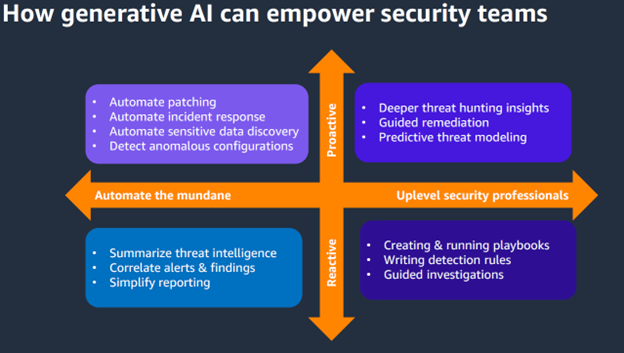
Another customer, CyberAgent, is using AWS to showcase how generative AI can also empower security teams. According to Dickson, generative AI can help security teams in different ways, from automating the mundane to uplevelling security professionals. It can also help security teams be both proactive and reactive, as seen in Figure 4.
CyberAgent is proving just how empowering generative AI can be to security teams by developing a generative AI-powered “security concierge” chatbot service—using AWS, of course. This service integrates with in-house systems such as Slack and is expected to handle more than half of a security team’s regular inquiries, thus freeing them up to actually do value-adding work.
Employees can also ask this security concierge for security advice in their natural language and receive immediate responses afterwards. In turn, security teams can focus on securing their environment and resolving important security alerts while automating troubleshooting tasks. All this, of course, is being made possible by innovating with generative AI in AWS.
Indeed, AWS is the most secure cloud—especially for generative AI. This is why customers are building generative AI applications on AWS, knowing fully well that they can do so safely and securely thanks to AWS’s unyielding commitment to security.
It is, after all, the company’s top priority.




